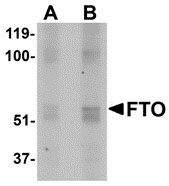
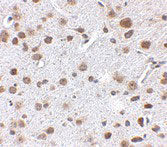
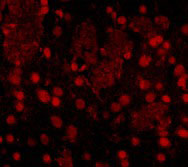
FTO Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, E, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9C0B1 |
| Other Accession | Q9C0B1, 148841515 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 58282 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Application Notes | FTO antibody can be used for detection of FTO by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 2.5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 79068 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase FTO, 1.14.11.-, Fat mass and obesity-associated protein, FTO, KIAA1752 |
| Target/Specificity | FTO; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | FTO antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | FTO Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | FTO {ECO:0000303|PubMed:17496892, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:24678} |
|---|---|
| Function | RNA demethylase that mediates oxidative demethylation of different RNA species, such as mRNAs, tRNAs and snRNAs, and acts as a regulator of fat mass, adipogenesis and energy homeostasis (PubMed:22002720, PubMed:25452335, PubMed:26457839, PubMed:26458103, PubMed:28002401, PubMed:30197295). Specifically demethylates N(6)- methyladenosine (m6A) RNA, the most prevalent internal modification of messenger RNA (mRNA) in higher eukaryotes (PubMed:22002720, PubMed:25452335, PubMed:26457839, PubMed:26458103, PubMed:30197295). M6A demethylation by FTO affects mRNA expression and stability (PubMed:30197295). Also able to demethylate m6A in U6 small nuclear RNA (snRNA) (PubMed:30197295). Mediates demethylation of N(6),2'-O- dimethyladenosine cap (m6A(m)), by demethylating the N(6)- methyladenosine at the second transcribed position of mRNAs and U6 snRNA (PubMed:28002401, PubMed:30197295). Demethylation of m6A(m) in the 5'-cap by FTO affects mRNA stability by promoting susceptibility to decapping (PubMed:28002401). Also acts as a tRNA demethylase by removing N(1)-methyladenine from various tRNAs (PubMed:30197295). Has no activity towards 1-methylguanine (PubMed:20376003). Has no detectable activity towards double-stranded DNA (PubMed:20376003). Also able to repair alkylated DNA and RNA by oxidative demethylation: demethylates single-stranded RNA containing 3-methyluracil, single- stranded DNA containing 3-methylthymine and has low demethylase activity towards single-stranded DNA containing 1-methyladenine or 3- methylcytosine (PubMed:18775698, PubMed:20376003). Ability to repair alkylated DNA and RNA is however unsure in vivo (PubMed:18775698, PubMed:20376003). Involved in the regulation of fat mass, adipogenesis and body weight, thereby contributing to the regulation of body size and body fat accumulation (PubMed:18775698, PubMed:20376003). Involved in the regulation of thermogenesis and the control of adipocyte differentiation into brown or white fat cells (PubMed:26287746). Regulates activity of the dopaminergic midbrain circuitry via its ability to demethylate m6A in mRNAs (By similarity). Plays an oncogenic role in a number of acute myeloid leukemias by enhancing leukemic oncogene-mediated cell transformation: acts by mediating m6A demethylation of target transcripts such as MYC, CEBPA, ASB2 and RARA, leading to promote their expression (PubMed:28017614, PubMed:29249359). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Nucleus speckle. Cytoplasm Note=Localizes mainly in the nucleus, where it is able to demethylate N(6)-methyladenosine (m6A) and N(6),2'-O-dimethyladenosine cap (m6A(m)) in U6 small nuclear RNA (snRNA), N(1)-methyladenine from tRNAs and internal m6A in mRNAs (PubMed:30197295). In the cytoplasm, mediates demethylation of m6A and m6A(m) in mRNAs and N(1)-methyladenine from tRNAs (PubMed:30197295). |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitously expressed, with relatively high expression in adrenal glands and brain; especially in hypothalamus and pituitary (PubMed:17434869, PubMed:17496892). Highly expressed in highly expressed in acute myeloid leukemias (AML) with t(11;11)(q23;23) with KMT2A/MLL1 rearrangements, t(15;17)(q21;q21)/PML-RARA, FLT3-ITD, and/or NPM1 mutations (PubMed:28017614). |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
FTO Antibody: Rising obesity rates are rapidly becoming a growing health concern in the developing world. The fat mass and obesity associated gene (FTO) is the first gene discovered to contribute to common forms of human obesity. FTO is a member of the non-heme dioxygenase superfamily, encoding a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent nucleic acid demethylase whose mRNA is widely expressed, especially in neurons of feeding-related nuclei of the brain. FTO mRNA in the arcuate nucleus in mice is up-regulated by feeding and down-regulated during fasting, although the opposite pattern has been observed in rats. At least four isoforms of FTO are known to exist.
REFERENCES
Scuteri A, Sanna S, Chen W-M, et al. Genome-wide association scan shows genetic variants in the FTO gene are associated with obesity-related traits. PloS Genet.2007; 3:e115.
Gerken T, Girard CA, Tung YCL, et al. The obesity-associated FTO gene encodes a 2-oxyglutarate-dependent nucleic acid demethylase. Science2007; 318:1469-72.
Fredriksson R, Hagglund M, Olszewski PK, et al. The obesity gene, FTO, is of ancient origin, upregulated during food deprivation and expressed in neurons of feeding-related nuclei of the brain. Endocrinology2008; 149:2062-71.
Stratigopoulous G, Padilla S, Leduc CA, et al. Regulation of FTO/FTM gene expression in mice and humans. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol.2008; 294:R1185-96.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。