NOD1 Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9Y239 |
| Other Accession | Q9Y239, 20137579 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 107691 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
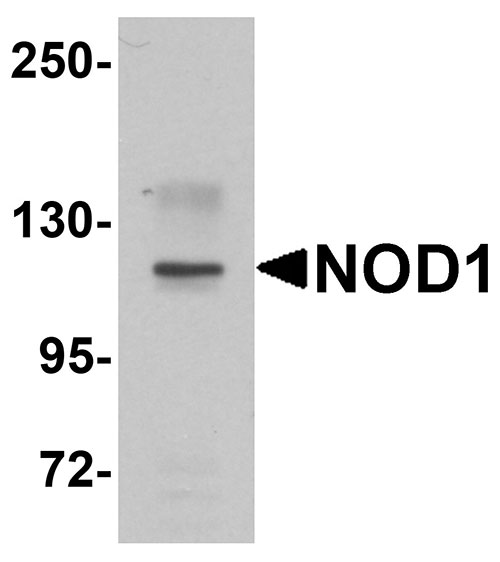
| Application Notes | NOD1 antibody can be used for detection of NOD1 by Western blot at 1 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 10392 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 1, Caspase recruitment domain-containing protein 4, NOD1, CARD4 |
| Target/Specificity | NOD1; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | NOD1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | NOD1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | NOD1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:10329646, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:16390} |
|---|---|
| Function | Pattern recognition receptor (PRR) that detects bacterial peptidoglycan fragments and other danger signals and thus participates in both innate and adaptive immune responses (PubMed:11058605, PubMed:12791997, PubMed:12796777, PubMed:15044951, PubMed:16172124, PubMed:19043560, PubMed:22672233, PubMed:27099311). Specifically recognizes and binds gamma-D-glutamyl-meso-diaminopimelic acid (iE- DAP), a dipeptide present in peptidoglycan of Gram-negative bacteria (PubMed:12791997, PubMed:12796777, PubMed:12871942, PubMed:16172124, PubMed:16211083). Preferentially binds iE-DAP in tripeptide-containing muropeptides (MurNAc-TriDAP or TriDAP) (PubMed:16211083). Ligand binding triggers oligomerization that facilitates the binding and subsequent activation of the proximal adapter receptor-interacting RIPK2 (PubMed:12791997, PubMed:12796777, PubMed:17054981). Following recruitment, RIPK2 undergoes 'Met-1'- (linear) and 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination by E3 ubiquitin-protein ligases XIAP, BIRC2, BIRC3 and the LUBAC complex, becoming a scaffolding protein for downstream effectors, triggering activation of the NF-kappa-B and MAP kinases signaling (PubMed:10880512, PubMed:12791997, PubMed:19043560). This in turn leads to the transcriptional activation of hundreds of genes involved in immune response (PubMed:10880512, PubMed:19043560). Also acts as a regulator of antiviral response elicited by dsRNA and the expression of RLR pathway members by targeting IFIH1 and TRAF3 to modulate the formation of IFIH1-MAVS and TRAF3-MAVS complexes leading to increased transcription of type I IFNs (PubMed:32169843). Also acts as a regulator of autophagy via its interaction with ATG16L1, possibly by recruiting ATG16L1 at the site of bacterial entry (By similarity). Besides recognizing pathogens, also involved in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response: acts by sensing and binding to the cytosolic metabolite sphingosine-1-phosphate generated in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress, initiating an inflammation process that leads to activation of the NF-kappa-B and MAP kinases signaling (PubMed:27007849, PubMed:33942347). In addition, plays a role in insulin trafficking in beta cells in a cell-autonomous manner (By similarity). Mechanistically, upon recognizing cognate ligands, NOD1 and RIPK2 localize to insulin vesicles where they recruit RAB1A to direct insulin trafficking through the cytoplasm (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Lipid-anchor. Apical cell membrane. Basolateral cell membrane. Cytoplasm. Note=Detected in the cytoplasm and at the cell membrane (PubMed:31649195). Following bacterial infection, localizes to bacterial entry sites in the cell membrane (PubMed:31649195). Recruited to the basolateral and apical membranes in polarized epithelial cells (PubMed:19043560) |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in adult heart, skeletal muscle, pancreas, spleen and ovary (PubMed:10224040). Also detected in placenta, lung, liver, kidney, thymus, testis, small intestine and colon (PubMed:10224040). |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
NOD1 Antibody: NOD1 is a member of the NOD (nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain) family, a group of proteins that are involved in innate immune defense. NOD1 contains an N-terminal caspase recruitment domain (CARD), a centrally located nucleotide-binding domain (NBD), and ten tandem leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) in its C-terminus. The CARD is involved in apoptotic signaling, and NOD1 activates caspase-9 and NF-κB. LRRs participate in protein-protein interactions, and mutations in the NBD may affect the process of oligomerization and subsequent function of the LRR domain. This protein is an intracellular pattern-recognition receptor (PRR) that initiates inflammation in response to a subset of bacteria through the detection of bacterial diaminopimelic acid.
REFERENCES
Kufer TA, Banks DJ, and Philpott DJ. Innate immune sensing of microbes by Nod proteins. Ann. NY Acad. Sci.2006; 1072:19-27.
Inohara N, Koseki T, del Peso L, et al. Nod1, an Apaf-1-like activator of caspase-9 and nuclear factor-kappaB. J. Biol. Chem.1999; 274:14560-7.
Chamaillard M, Hashimoto M, Horie Y, et al. An essential role for NOD1 in host recognition of bacterial peptidoglycan containing diaminopimelic acid. Nat. Immunol.2003; 4:702-7.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。