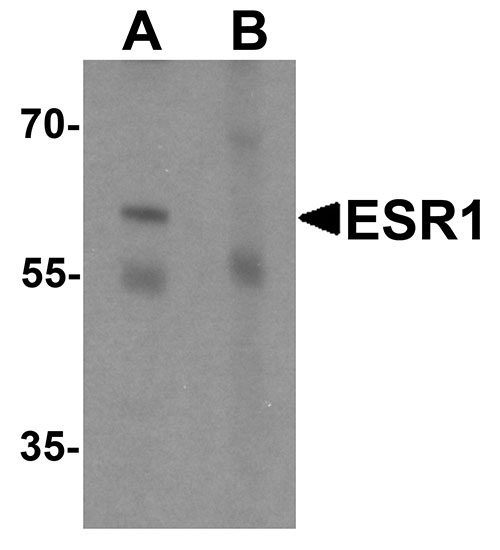
ESR1 Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, E, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P03372 |
| Other Accession | NP_001116214, 170295804 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 66216 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Application Notes | ESR1 antibody can be used for detection of ESR1 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 2099 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Estrogen receptor, ER, ER-alpha, Estradiol receptor, Nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group A member 1, ESR1, ESR, NR3A1 |
| Target/Specificity | ESR1; ESR1 antibody is human, mouse and rat reactive. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | ESR1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | ESR1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | ESR1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | ESR, NR3A1 |
| Function | Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE- independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa- B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3 (PubMed:17922032). Maintains neuronal survival in response to ischemic reperfusion injury when in the presence of circulating estradiol (17-beta-estradiol/E2) (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | [Isoform 1]: Nucleus {ECO:0000255|PROSITE- ProRule:PRU00407, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12682286, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20074560}. Cytoplasm. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Note=A minor fraction is associated with the inner membrane Nucleus. Golgi apparatus. Cell membrane. Note=Colocalizes with ZDHHC7 and ZDHHC21 in the Golgi apparatus where most probably palmitoylation occurs. Associated with the plasma membrane when palmitoylated |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed (PubMed:10970861). Not expressed in the pituitary gland (PubMed:10970861) |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
ESR1 Antibody: Estrogen receptors (ER) are members of the steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily of ligand-activated transcription factors (1). Estrogen receptors, including ESR1, also known as ER-alpha and ESR2 (ER-beta), contain DNA binding and ligand binding domains and are critically involved in regulating the normal function of reproductive tissues. ESR1 is a widely expressed nuclear protein and serves as a strong activator of estrogen responsive genes (1,2). Phosphorylation of serines 104 and 106, located in the N-terminal transcription activation function-1 domain (AF-1), plays a large role in regulating ER alpha activity (3).
REFERENCES
Pakdel F, Reese JC, and Katzenellenbogen BS. Identification of charged residues in an N- terminal portion of the hormone-binding domain of the human estrogen receptor important in transcriptional activity of the receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 1993; 7:1408-17.
Sheeler CQ, Singleton DW, and Khan SA. Mutation of serines 104, 106, and 118 inhibits dimerization of the human estrogen receptor in yeast. Endocr. Res. 2003; 29:237-55.
Rogatsky I, Trowbridge JM, and Garabedian MJ. Potentiation of human estrogen receptor alpha transcriptional activation through phosphorylation of serines 104 and 106 by the cyclin A-CDK2 complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1999; 274:22296-302.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。