TRPV4 Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, E, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9HBA0 |
| Other Accession | NP_067638, 22547184 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 98281 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
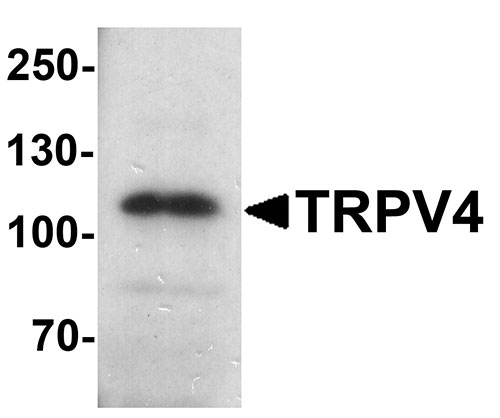
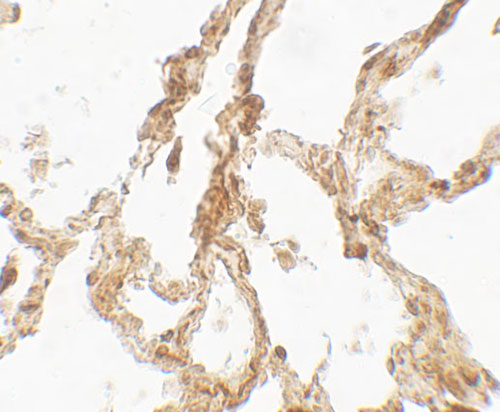
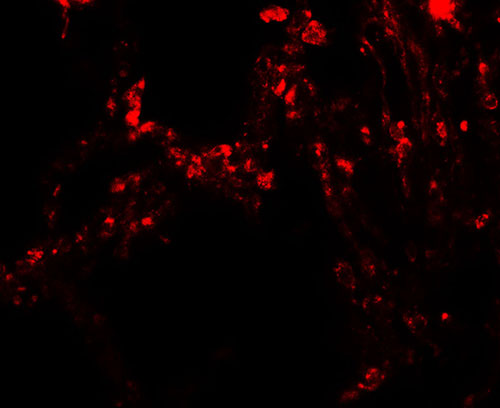
| Application Notes | TRPV4 antibody can be used for detection of TRPV4 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml. Antibody can also be used for Immunohistochemistry starting at 5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 59341 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 4, TrpV4, Osm-9-like TRP channel 4, OTRPC4, Transient receptor potential protein 12, TRP12, Vanilloid receptor-like channel 2, Vanilloid receptor-like protein 2, VRL-2, Vanilloid receptor-related osmotically-activated channel, VR-OAC, TRPV4, VRL2, VROAC |
| Target/Specificity | TRPV4; TRPV4 antibody is human specific. At least six isoforms of TRPV4 are known to exist. This antibody is predicted to not cross-react with other TRP protein family members. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | TRPV4 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | TRPV4 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | TRPV4 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | VRL2, VROAC |
| Function | Non-selective calcium permeant cation channel involved in osmotic sensitivity and mechanosensitivity (PubMed:16293632, PubMed:18695040, PubMed:18826956, PubMed:22526352, PubMed:23136043, PubMed:29899501). Activation by exposure to hypotonicity within the physiological range exhibits an outward rectification (PubMed:18695040, PubMed:18826956, PubMed:29899501). Also activated by heat, low pH, citrate and phorbol esters (PubMed:16293632, PubMed:18695040, PubMed:18826956, PubMed:20037586, PubMed:21964574, PubMed:25256292). Increase of intracellular Ca(2+) potentiates currents. Channel activity seems to be regulated by a calmodulin-dependent mechanism with a negative feedback mechanism (PubMed:12724311, PubMed:18826956). Promotes cell-cell junction formation in skin keratinocytes and plays an important role in the formation and/or maintenance of functional intercellular barriers (By similarity). Acts as a regulator of intracellular Ca(2+) in synoviocytes (PubMed:19759329). Plays an obligatory role as a molecular component in the nonselective cation channel activation induced by 4-alpha-phorbol 12,13-didecanoate and hypotonic stimulation in synoviocytes and also regulates production of IL-8 (PubMed:19759329). Together with PKD2, forms mechano- and thermosensitive channels in cilium (PubMed:18695040). Negatively regulates expression of PPARGC1A, UCP1, oxidative metabolism and respiration in adipocytes (By similarity). Regulates expression of chemokines and cytokines related to pro-inflammatory pathway in adipocytes (By similarity). Together with AQP5, controls regulatory volume decrease in salivary epithelial cells (By similarity). Required for normal development and maintenance of bone and cartilage (PubMed:26249260). In its inactive state, may sequester DDX3X at the plasma membrane. When activated, the interaction between both proteins is affected and DDX3X relocalizes to the nucleus (PubMed:29899501). In neurons of the central nervous system, could play a role in triggering voluntary water intake in response to increased sodium concentration in body fluid (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane. Apical cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell junction, adherens junction {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9EPK8}. Cell projection, cilium. Note=Assembly of the putative homotetramer occurs primarily in the endoplasmic reticulum (PubMed:16293632, PubMed:20037587, PubMed:20037588). Localization to the cell membrane is inhibited by WNK kinases (WNK1, WNK2, WNK3 or WNK4) in a kinase-independent mechanism (PubMed:16403833) [Isoform 5]: Cell membrane [Isoform 4]: Endoplasmic reticulum |
| Tissue Location | Found in the synoviocytes from patients with (RA) and without (CTR) rheumatoid arthritis (at protein level) |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
The transient receptor potential (TRP) protein family consists of a diverse group of cation channels functioning in a variety of homeostatic and regulatory pathways. Four subfamilies exist, based on channel domain homology: C type (canonical), V type (vanilloid receptor related), M type (melastatin related) and P type (PKD) (1). TRPV4, belongs to the V type subfamily and plays a role in systemic osmoregulation (2,3). TRPV4 is a calcium channel multi-pass membrane protein activated by various stimuli, including thermal stress, fatty acid metabolites and hypotonicity (3). TRPV4 is highly expressed in lung and kidney and widely expressed in brain. It plays an important role in regulating neural excitability (4).
REFERENCES
Birnbaumer L, Yildirim E and Abramowitz J. A comparison of the genes coding for canonical TRP channels and their M, V and P relatives. Cell Calcium 2003; 33:419-32.
Alessandri-Haber N, Dina OA, Yeh JJ, et al. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 is essential in chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain in the rat. J. Neurosci. 2004; 24:4444-52.
Liedtke W. TRPV4 plays an evolutionary conserved role in the transduction of osmotic and mechanical stimuli in live animals. J. Physiol. 2005; 567:53-8.
Shibasaki K, Suzuki M, Mizuno A, et al. Effects of body temperature on neural activity in the hippocampus: regulation of resting membrane potentials by transient receptor potential vanilloid 4. J. Neurosci. 2007; 27:1566–75.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。