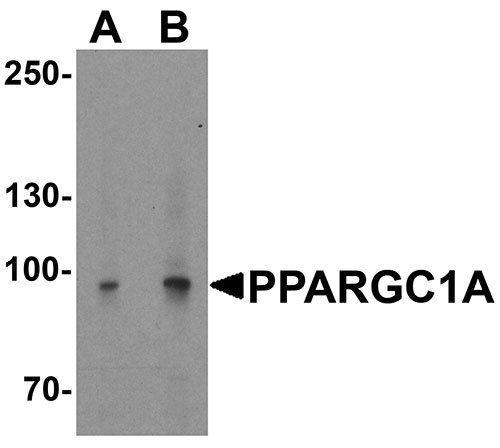
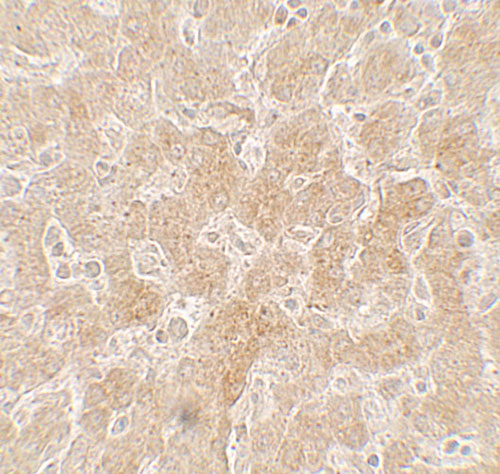
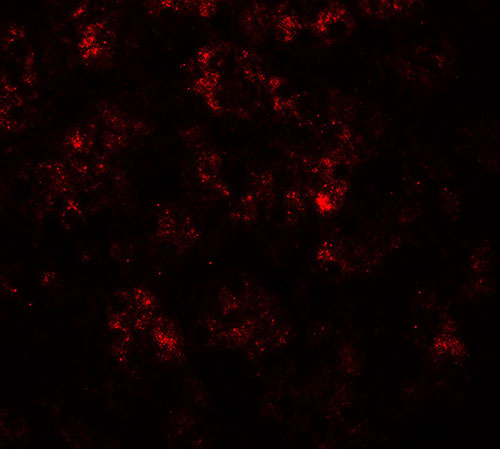
PPARGC1A Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, E, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9UBK2 |
| Other Accession | NP_037393, 7019499 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 91027 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Application Notes | PPARGC1A antibody can be used for detection of PPARGC1A by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml. Antibody can also be used for Immunohistochemistry starting at 5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 10891 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha, PGC-1-alpha, PPAR-gamma coactivator 1-alpha, PPARGC-1-alpha, Ligand effect modulator 6, PPARGC1A, LEM6, PGC1, PGC1A, PPARGC1 |
| Target/Specificity | PPARGC1A; PPARGC1A antibody is human, mouse and rat reactive. At least three isoforms of PPARGC1A are known to exist; this antibody only detects the longest isoform. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | PPARGC1A antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | PPARGC1A Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | PPARGC1A |
|---|---|
| Function | Transcriptional coactivator for steroid receptors and nuclear receptors (PubMed:10713165, PubMed:20005308, PubMed:21376232, PubMed:28363985, PubMed:32433991). Greatly increases the transcriptional activity of PPARG and thyroid hormone receptor on the uncoupling protein promoter (PubMed:10713165, PubMed:20005308, PubMed:21376232). Can regulate key mitochondrial genes that contribute to the program of adaptive thermogenesis (PubMed:10713165, PubMed:20005308, PubMed:21376232). Plays an essential role in metabolic reprogramming in response to dietary availability through coordination of the expression of a wide array of genes involved in glucose and fatty acid metabolism (PubMed:10713165, PubMed:20005308, PubMed:21376232). Acts as a key regulator of gluconeogenesis: stimulates hepatic gluconeogenesis by increasing the expression of gluconeogenic enzymes, and acting together with FOXO1 to promote the fasting gluconeogenic program (PubMed:16753578, PubMed:23142079). Induces the expression of PERM1 in the skeletal muscle in an ESRRA- dependent manner (PubMed:23836911). Also involved in the integration of the circadian rhythms and energy metabolism (By similarity). Required for oscillatory expression of clock genes, such as BMAL1 and NR1D1, through the coactivation of RORA and RORC, and metabolic genes, such as PDK4 and PEPCK (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | [Isoform 1]: Nucleus. Nucleus, PML body {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O70343} [Isoform B4-8a]: Cytoplasm. Nucleus [Isoform 9]: Nucleus |
| Tissue Location | Heart, skeletal muscle, liver and kidney. Expressed at lower levels in brain and pancreas and at very low levels in the intestine and white adipose tissue. In skeletal muscle, levels were lower in obese than in lean subjects and fasting induced a 2-fold increase in levels in the skeletal muscle in obese subjects |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PPARGC1A), also known as LEM-6, is a transcriptional coactivator that regulates the genes involved in energy metabolism (1). PPARGC1A interacts with PPARgamma, which permits the interaction of PPARGC1A with multiple transcription factors. PPARGC1A can interact with, and regulate the activities of, cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) and nuclear respiratory factors (NRFs). It provides a direct link between external physiological stimuli and the regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis, and is a major factor that regulates muscle fiber type determination (2). PPARGC1A may be also involved in the development of obesity (3).
REFERENCES
Tsuemi T and La Spada AR. PGC-1a at the intersection of bioenergetics regulation and neuron function: from Huntington’s disease to Parkinson’s disease and beyond. Prog. Neurobiol. 2012; 97:142-51.
Kang C and Li Ji L. Role of PGC-1a signaling in skeletal muscle health and disease. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2012; 1271:110-7.
Liu C and Lin JD. PGC-1 coactivators in the control of energy metabolism. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2011; 43:248-57.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。