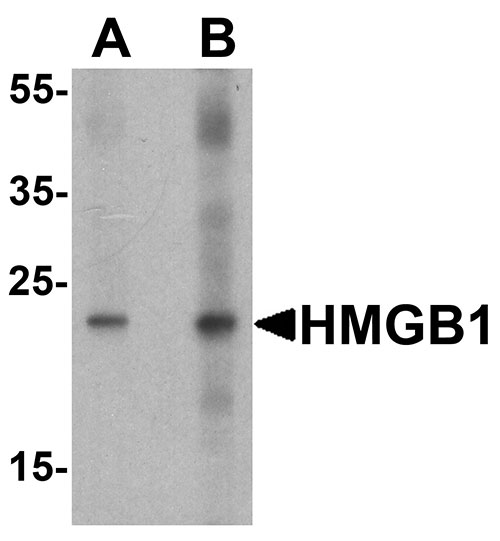
HMGB1 Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, E, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P09429 |
| Other Accession | NP_002119, 4504425 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 24894 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Application Notes | HMGB1 antibody can be used for detection of HMGB1 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml. Antibody can also be used for Immunohistochemistry starting at 5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 3146 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | High mobility group protein B1, High mobility group protein 1, HMG-1, HMGB1, HMG1 |
| Target/Specificity | HMGB1; HMGB1 antibody is human, mouse and rat reactive. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | HMGB1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | HMGB1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | HMGB1 (HGNC:4983) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | HMG1 |
| Function | Multifunctional redox sensitive protein with various roles in different cellular compartments. In the nucleus is one of the major chromatin-associated non-histone proteins and acts as a DNA chaperone involved in replication, transcription, chromatin remodeling, V(D)J recombination, DNA repair and genome stability (PubMed:33147444). Proposed to be an universal biosensor for nucleic acids. Promotes host inflammatory response to sterile and infectious signals and is involved in the coordination and integration of innate and adaptive immune responses. In the cytoplasm functions as a sensor and/or chaperone for immunogenic nucleic acids implicating the activation of TLR9-mediated immune responses, and mediates autophagy. Acts as a danger-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecule that amplifies immune responses during tissue injury (PubMed:27362237). Released to the extracellular environment can bind DNA, nucleosomes, IL-1 beta, CXCL12, AGER isoform 2/sRAGE, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and lipoteichoic acid (LTA), and activates cells through engagement of multiple surface receptors (PubMed:34743181). In the extracellular compartment fully reduced HMGB1 (released by necrosis) acts as a chemokine, disulfide HMGB1 (actively secreted) as a cytokine, and sulfonyl HMGB1 (released from apoptotic cells) promotes immunological tolerance (PubMed:23446148, PubMed:23519706, PubMed:23994764, PubMed:25048472). Has proangiogdenic activity (By similarity). May be involved in platelet activation (By similarity). Binds to phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamide (By similarity). Bound to RAGE mediates signaling for neuronal outgrowth (By similarity). May play a role in accumulation of expanded polyglutamine (polyQ) proteins such as huntingtin (HTT) or TBP (PubMed:23303669, PubMed:25549101). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Chromosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P10103, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63159, ECO:0000305}. Cytoplasm. Secreted {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63158, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12231511, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14532127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15944249, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19811284, ECO:0000269|PubMed:22869893, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33147444}. Cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63158, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63159, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11154118}; Peripheral membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63158, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63159, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11154118}; Extracellular side {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63158, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63159, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11154118}. Endosome {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63158} Endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63158}. Note=In basal state predominantly nuclear. Shuttles between the cytoplasm and the nucleus (PubMed:12231511, PubMed:17114460). Translocates from the nucleus to the cytoplasm upon autophagy stimulation (PubMed:20819940). Release from macrophages in the extracellular milieu requires the activation of NLRC4 or NLRP3 inflammasomes (By similarity). Passively released to the extracellular milieu from necrotic cells by diffusion, involving the fully reduced HGMB1 which subsequently gets oxidized (PubMed:19811284) Also released from apoptotic cells (PubMed:16855214, PubMed:18631454) Active secretion from a variety of immune and non-immune cells such as macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils, dendritic cells and natural killer cells in response to various stimuli such as LPS and cytokines involves a nonconventional secretory process via secretory lysosomes (PubMed:12231511, PubMed:14532127, PubMed:15944249). Secreted by plasma cells in response to LPS (By similarity). Found on the surface of activated platelets (PubMed:11154118). An increased chromatin association is observed when associated with the adenovirus protein pVII (PubMed:27362237). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P63158, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11154118, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12231511, ECO:0000269|PubMed:14532127, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15944249, ECO:0000269|PubMed:16855214, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17114460, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18631454, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19811284, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20819940, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27362237, ECO:0000305|PubMed:20123072} |
| Tissue Location | Ubiquitous. Expressed in platelets (PubMed:11154118). |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
The high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) protein was originally identified as a highly conserved nuclear DNA-binding protein that participates in DNA replication, repair and transcriptional regulation of gene expression (1,2). However, HMGB1 has more recently emerged as an extracellularly released mediator of inflammation and repair responses in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endotoxemia and sepsis (3). HMGB1 has also been suggested to induce secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines by inducing NF-kB signaling downstream of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4 activation (4).
REFERENCES
Smerdon MJ and Isenberg I. Interactions between the subfractions of calf thymus H1 and nonhistone chromosomal proteins HMG1 and HMG2. Biochemistry 1976; 15:4242-7.
Stros M. HMGB proteins: interactions with DNA and chromatin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2010; 1799:101-13.
Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, , et al. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science 1999; 285:248-51.
van Zoelen MA, Yang H, Florquin S, et al. Role of toll-like receptors 2 and 4, and the receptor for advanced glycation end products in high-mobility group box 1-induced inflammation in vivo. Shock 2009; 31:280-4.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。