LIMA1 Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, E, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9UHB6 |
| Other Accession | NP_001107018, 165905589 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 85226 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
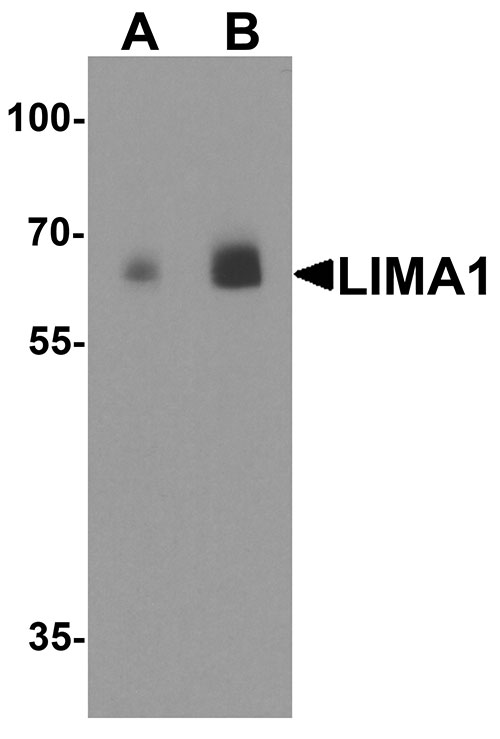
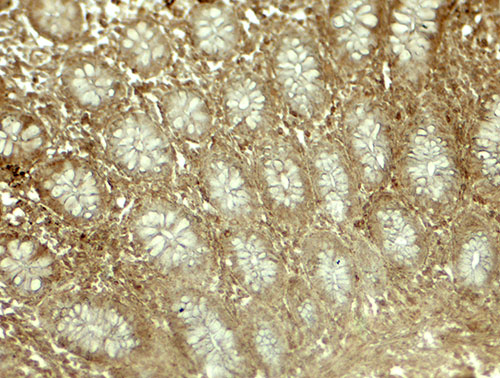
| Application Notes | LIMA1 antibody can be used for detection of LIMA1 by Western blot at 0.5 - 1 µg/ml. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 51474 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | LIM domain and actin-binding protein 1, Epithelial protein lost in neoplasm, LIMA1, EPLIN, SREBP3 |
| Target/Specificity | LIMA1; LIMA1 antibody is human specific. At least four isoforms of LIMA1 are known to exist; this antibody will only detect the three largest isoforms. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | LIMA1 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | LIMA1 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | LIMA1 (HGNC:24636) |
|---|---|
| Function | Actin-binding protein involved in actin cytoskeleton regulation and dynamics. Increases the number and size of actin stress fibers and inhibits membrane ruffling. Inhibits actin filament depolymerization. Bundles actin filaments, delays filament nucleation and reduces formation of branched filaments (PubMed:12566430, PubMed:33999101). Acts as a negative regulator of primary cilium formation (PubMed:32496561). Plays a role in cholesterol homeostasis. Influences plasma cholesterol levels through regulation of intestinal cholesterol absorption. May act as a scaffold protein by regulating NPC1L1 transportation, an essential protein for cholesterol absorption, to the plasma membrane by recruiting MYO5B to NPC1L1, and thus facilitates cholesterol uptake (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Cell junction, focal adhesion. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, stress fiber. Cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ERG0}. Cell projection, ruffle. Cell projection, lamellipodium. Note=Expressed in the brush border membrane of the small intestine and colocalizes with NPC1L1 and MYO5B (PubMed:29880681). Colocalizes with PXN at focal adhesions in mesangial cells (PubMed:24694988). Colocalizes with actin stress fibers in quiescent cells. PDGF stimulation induced disassembly of stress fibers and formation of peripheral and dorsal ruffles, where LIMA1 is relocalized (By similarity). Localized at the lamellipodia, just behind lamellipodia actin ruffles (PubMed:33999101) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9ERG0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24694988, ECO:0000269|PubMed:29880681, ECO:0000269|PubMed:33999101} |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in placenta, kidney, pancreas, prostate, ovary, spleen and heart. Also detected in lung, liver, brain, skeletal muscle, thymus, testis and intestine. Not detected in leukocytes. Isoform Beta expressed generally at very low levels Isoform Alpha abundant in epithelial cells from mammary gland, prostate and in normal oral keratinocytes. Low levels in aortic endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts. Not detectable in myocardium |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
The Lim domain and actin-binding protein 1 (LIMA1) is cytoskeleton-associated protein that inhibits actin filament depolymerization and cross-links filaments in bundles and is downregulated in some cancer cell lines (1,2). LIMA1 is also a key molecule linking the cadherin-catenin complex to the actin cytoskeleton (3). Recent studies have shown that EGF activates ERK1/2-dependent phosphorylation, ubiquitination and degradation of LIMA1, leading to increased invasiveness and metastasis of metastatic prostate cancer models (4).
REFERENCES
Maul RS and Chang DD. EPLIN, epithelial protein lost in neoplasm. Oncogene 1999; 18:7838-41.
Maul RS, Song Y, Amann KJ, et al. EPLIN regulates actin dynamics by cross-linking and stabilizing filaments. J. Cell Biol. 2003; 160:399-407.
Abe K and Takeichi M. EPLIN mediates linkage of the cadherin catenin complex to F-actin and stabilizes the circumferential actin belt. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008; 105:13-9.
Zhang S, Wang X, Iqval S, et al. Epidermal growth factor promotes protein degradation of epithelial protein lost in neoplasm (EPLIN), a putative metastasis suppressor, during epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Biol. Chem. 2013; 288:1469-79.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。