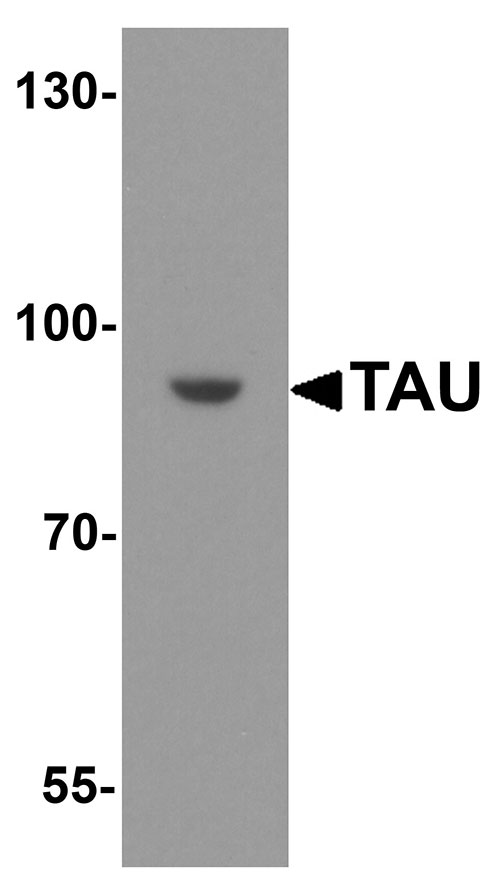
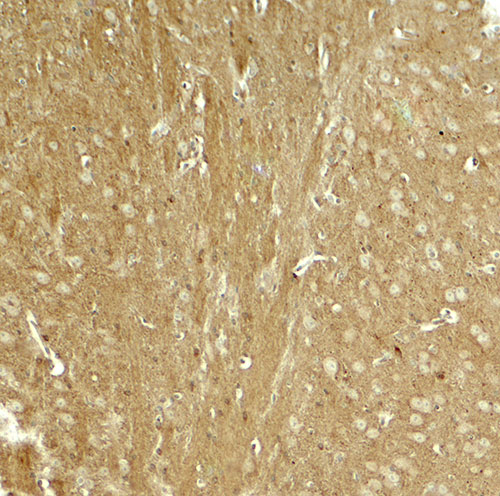
TAU Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, E, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P10636 |
| Other Accession | NP_058519, 294862261 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 78928 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Application Notes | TAU antibody can be used for detection of TAU by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 5 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 4137 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Microtubule-associated protein tau, Neurofibrillary tangle protein, Paired helical filament-tau, PHF-tau, MAPT, MAPTL, MTBT1, TAU |
| Target/Specificity | TAU; TAU antibody is human, mouse and rat reactive. Multiple isoforms of TAU are known to exist; this antibody will only detect the two longest isoforms. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | TAU antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | TAU Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | MAPT (HGNC:6893) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | MAPTL, MTBT1, TAU |
| Function | Promotes microtubule assembly and stability, and might be involved in the establishment and maintenance of neuronal polarity (PubMed:21985311). The C-terminus binds axonal microtubules while the N-terminus binds neural plasma membrane components, suggesting that tau functions as a linker protein between both (PubMed:21985311, PubMed:32961270). Axonal polarity is predetermined by TAU/MAPT localization (in the neuronal cell) in the domain of the cell body defined by the centrosome. The short isoforms allow plasticity of the cytoskeleton whereas the longer isoforms may preferentially play a role in its stabilization. |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytosol. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein; Cytoplasmic side. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cell projection, axon. Cell projection, dendrite. Secreted Note=Mostly found in the axons of neurons, in the cytosol and in association with plasma membrane components (PubMed:10747907). Can be secreted; the secretion is dependent on protein unfolding and facilitated by the cargo receptor TMED10; it results in protein translocation from the cytoplasm into the ERGIC (endoplasmic reticulum- Golgi intermediate compartment) followed by vesicle entry and secretion (PubMed:32272059). |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in neurons. Isoform PNS-tau is expressed in the peripheral nervous system while the others are expressed in the central nervous system |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
The microtubial-associated protein TAU (MAPT), more commonly known as TAU, is is normally a highly soluble protein found predominantly in neurons (1), but accumulations of highly phosphorylated tau protein aggregates are observed in several neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration, and frontotemporal lobar dementia. It was thought that these pathological tau aggregates were the toxic form of tau, but recent studies indicate that soluble and highly phosphorylated tau species are more closely associated with synaptic dysfunction and cell loss (2,3). Mutations in the TAU gene have also been associated with several of these neurodegenerative diseases (4).
REFERENCES
Dotti CG, Banker GA, and Binder LI. The expression and distribution of the microtubule-associated proteins tau and microtubule-associated protein 2 in hippocampal neurons in the rat in situ and in cell culture. Neuroscience 1987; 23:121-30.
Hanger DP, Brion JP, Gallo JM, et al. Tau in Alzheimer’s disease and Down’s syndrome is insoluble and abnormally phosphorylated. Biochem. J. 1991; 275:99–104.
Rocher AB, Crimins JL, Amatrudo JM, et al. Structural and functional changes in tau mutant mice neurons are not linked to the presence of NFTs. Exp. Neurol. 2010; 223:385–93.
Galimberti D and Scarpini E. Genetics and biology of Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. IInt. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2010; 3:129-43.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。