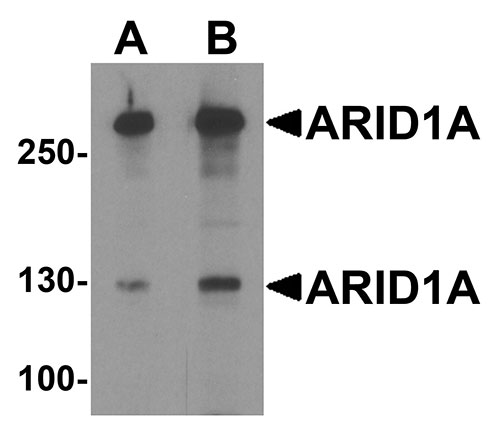
ARID1A Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O14497 |
| Other Accession | NP_006006, 21264565 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 242045 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Application Notes | ARID1A antibody can be used for detection of ARID1A by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 8289 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 1A, ARID domain-containing protein 1A, B120, BRG1-associated factor 250, BAF250, BRG1-associated factor 250a, BAF250A, Osa homolog 1, hOSA1, SWI-like protein, SWI/SNF complex protein p270, SWI/SNF-related, matrix-associated, actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily F member 1, hELD, ARID1A, BAF250, BAF250A, C1orf4, OSA1, SMARCF1 |
| Target/Specificity | ARID1A; ARID1A antibody is human, mouse and rat reactive. Multiple isoforms of ARID1A protein are known to exist. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | ARID1A antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | ARID1A Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | ARID1A |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | BAF250, BAF250A, C1orf4, OSA1, SMARCF1 |
| Function | Involved in transcriptional activation and repression of select genes by chromatin remodeling (alteration of DNA-nucleosome topology). Component of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes that carry out key enzymatic activities, changing chromatin structure by altering DNA-histone contacts within a nucleosome in an ATP-dependent manner. Binds DNA non-specifically. Belongs to the neural progenitors- specific chromatin remodeling complex (npBAF complex) and the neuron- specific chromatin remodeling complex (nBAF complex). During neural development a switch from a stem/progenitor to a postmitotic chromatin remodeling mechanism occurs as neurons exit the cell cycle and become committed to their adult state. The transition from proliferating neural stem/progenitor cells to postmitotic neurons requires a switch in subunit composition of the npBAF and nBAF complexes. As neural progenitors exit mitosis and differentiate into neurons, npBAF complexes which contain ACTL6A/BAF53A and PHF10/BAF45A, are exchanged for homologous alternative ACTL6B/BAF53B and DPF1/BAF45B or DPF3/BAF45C subunits in neuron-specific complexes (nBAF). The npBAF complex is essential for the self-renewal/proliferative capacity of the multipotent neural stem cells. The nBAF complex along with CREST plays a role regulating the activity of genes essential for dendrite growth (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus {ECO:0000255|PROSITE-ProRule:PRU00355, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11318604, ECO:0000269|PubMed:26614907} |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in spleen, thymus, prostate, testis, ovary, small intestine, colon, and PBL, and at a much lower level in heart, brain, placenta, lung, liver, skeletal muscle, kidney, and pancreas. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
The ARID1A protein is a member of the SWI/SNF family, whose members are thought to regulate transcription of certain genes by altering the chromatin structure around those genes. ARID1A is part of the large ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complex SNF/SWI, which is required for transcriptional activation of genes normally repressed by chromatin (1). It possesses a DNA-binding domain that can specifically bind an AT-rich DNA sequence known to be recognized by a SNF/SWI complex at the beta-globin locus. The C-terminus of the protein can stimulate glucocorticoid receptor-dependent transcriptional activation. It is thought that ARID1A confers specificity to the SNF/SWI complex and may recruit the complex to its targets through either protein-DNA or protein-protein interactions (2).
REFERENCES
Martens JA and Winston F. Recent advances in understanding chromatin remodeling by Swi/Snf complexes. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2003; 13:136-42.
Nie Z, Xue Y, Yang D, et al. A specificity and targeting subunit of a human SWI/SNF family-related chromatin-remodeling complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000; 20:8879-88.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.






















 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。