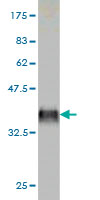
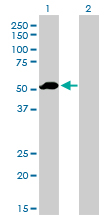
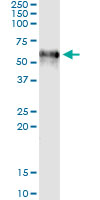
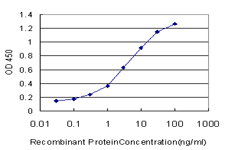
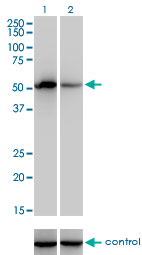
F9 Antibody (monoclonal) (M01)
Mouse monoclonal antibody raised against a partial recombinant F9.
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IP, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P00740 |
| Other Accession | NM_000133 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | mouse |
| Clonality | monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG1 Kappa |
| Clone Names | 2C9 |
| Calculated MW | 51778 Da |
| Gene ID | 2158 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Coagulation factor IX, Christmas factor, Plasma thromboplastin component, PTC, Coagulation factor IXa light chain, Coagulation factor IXa heavy chain, F9 |
| Target/Specificity | F9 (NP_000124, 96 a.a. ~ 190 a.a) partial recombinant protein with GST tag. MW of the GST tag alone is 26 KDa. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:500~1000 IP~~N/A E~~N/A |
| Format | Clear, colorless solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2 . |
| Storage | Store at -20°C or lower. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Precautions | F9 Antibody (monoclonal) (M01) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This gene encodes vitamin K-dependent coagulation factor IX that circulates in the blood as an inactive zymogen. This factor is converted to an active form by factor XIa, which excises the activation peptide and thus generates a heavy chain and a light chain held together by one or more disulfide bonds. The role of this activated factor IX in the blood coagulation cascade is to activate factor X to its active form through interactions with Ca+2 ions, membrane phospholipids, and factor VIII. Alterations of this gene, including point mutations, insertions and deletions, cause factor IX deficiency, which is a recessive X-linked disorder, also called hemophilia B or Christmas disease.
REFERENCES
Variation at the NFATC2 Locus Increases the Risk of Thiazolinedinedione-Induced Edema in the Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication (DREAM) Study. Bailey SD, et al. Diabetes Care, 2010 Jul 13. PMID 20628086.Genetic risk factors for hepatopulmonary syndrome in patients with advanced liver disease. Roberts KE, et al. Gastroenterology, 2010 Jul. PMID 20346360.Gene variants associated with venous thrombosis: confirmation in the MEGA study. Arellano AR, et al. J Thromb Haemost, 2010 May. PMID 20128871.Gene-centric association signals for lipids and apolipoproteins identified via the HumanCVD BeadChip. Talmud PJ, et al. Am J Hum Genet, 2009 Nov. PMID 19913121.Contribution of magnesium in binding of factor IXa to the phospholipid surface: implications for vitamin K-dependent coagulation proteins. Messer AS, et al. J Thromb Haemost, 2009 Dec. PMID 19817987.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。