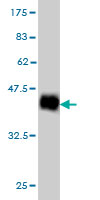
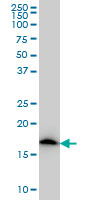
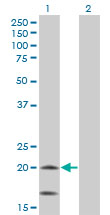
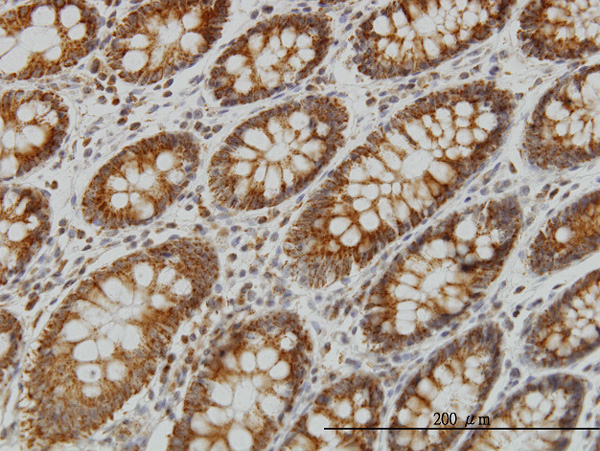
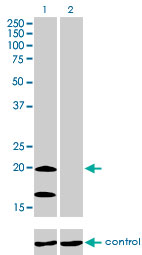
NDUFS4 Antibody (monoclonal) (M01)
Mouse monoclonal antibody raised against a partial recombinant NDUFS4.
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IHC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O43181 |
| Other Accession | NM_002495 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | mouse |
| Clonality | monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG2a Kappa |
| Clone Names | 1A1 |
| Calculated MW | 20108 Da |
| Gene ID | 4724 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] iron-sulfur protein 4, mitochondrial, Complex I-18 kDa, CI-18 kDa, Complex I-AQDQ, CI-AQDQ, NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 18 kDa subunit, NDUFS4 |
| Target/Specificity | NDUFS4 (NP_002486, 66 a.a. ~ 175 a.a) partial recombinant protein with GST tag. MW of the GST tag alone is 26 KDa. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:500~1000 IHC~~1:100~500 E~~N/A |
| Format | Clear, colorless solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2 . |
| Storage | Store at -20°C or lower. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Precautions | NDUFS4 Antibody (monoclonal) (M01) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
This gene encodes an accessory subunit of the mitochondrial membrane respiratory chain NADH dehydrogenase (Complex I), or NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase, the first multi-subunit enzyme complex of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Complex I plays a vital role in cellular ATP production, the primary source of energy for many crucial processes in living cells. It removes electrons from NADH and passes them by a series of different protein-coupled redox centers to the electron acceptor ubiquinone. In well-coupled mitochondria, the electron flux leads to ATP generation via the building of a proton gradient across the inner membrane. Complex I is composed of at least 41 subunits, of which 7 are encoded by the mitochondrial genome and the remainder by nuclear genes.
REFERENCES
NDUFS4 mutations cause Leigh syndrome with predominant brainstem involvement. Leshinsky-Silver E, et al. Mol Genet Metab, 2009 Jul. PMID 19364667.Association study between single-nucleotide polymorphisms in 199 drug-related genes and commonly measured quantitative traits of 752 healthy Japanese subjects. Saito A, et al. J Hum Genet, 2009 Jun. PMID 19343046.Polymorphisms in mitochondrial genes and prostate cancer risk. Wang L, et al. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, 2008 Dec. PMID 19064571.Oxidative stress, telomere length and biomarkers of physical aging in a cohort aged 79 years from the 1932 Scottish Mental Survey. Starr JM, et al. Mech Ageing Dev, 2008 Dec. PMID 18977241.The regulation of PTC containing transcripts of the human NDUFS4 gene of complex I of respiratory chain and the impact of pathological mutations. Panelli D, et al. Biochimie, 2008 Oct. PMID 18555024.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。