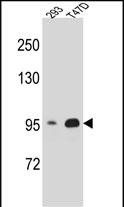
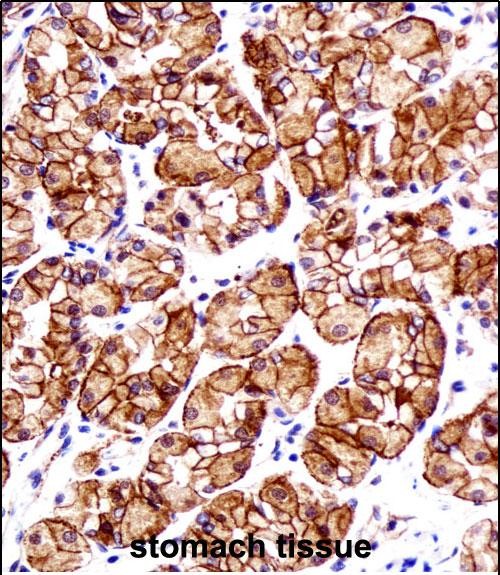
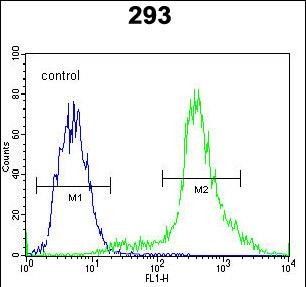
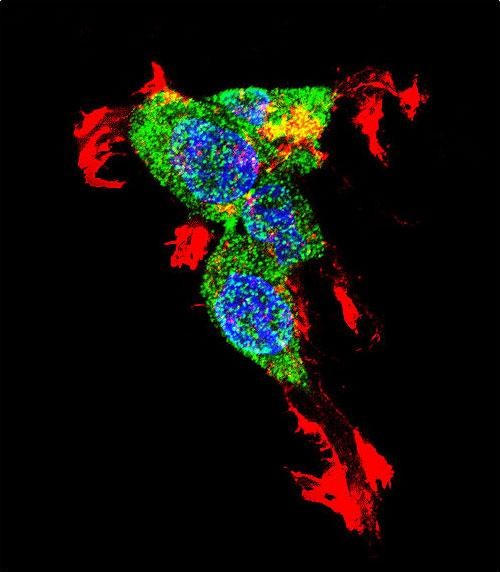
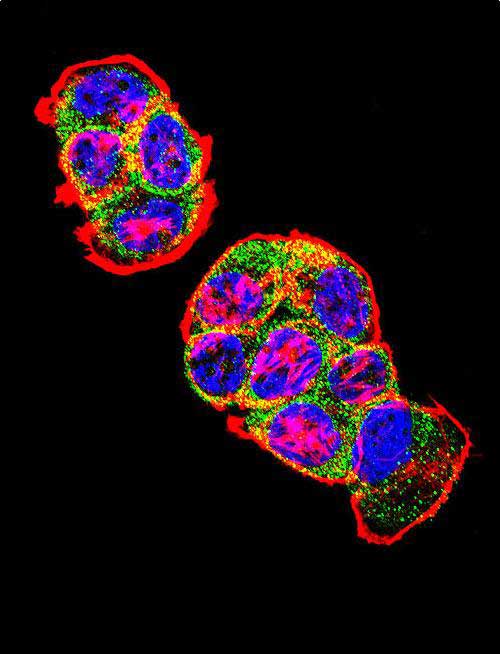
CTNNB1 Antibody (N-term)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IHC-P, FC, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P35222 |
| Other Accession | P26233, Q9WU82, Q02248, Q0VCX4, NP_001091679.1 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Predicted | Bovine, Mouse, Rat, Xenopus |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Clone Names | RB41155 |
| Calculated MW | 85497 Da |
| Antigen Region | 78-106 aa |
| Gene ID | 1499 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Catenin beta-1, Beta-catenin, CTNNB1, CTNNB |
| Target/Specificity | This CTNNB1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 78-106 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CTNNB1. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:2000 IHC-P~~1:100~500 FC~~1:50 IF~~1:50 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | CTNNB1 Antibody (N-term) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CTNNB1 (HGNC:2514) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | CTNNB |
| Function | Key downstream component of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway (PubMed:17524503, PubMed:18077326, PubMed:18086858, PubMed:18957423, PubMed:21262353, PubMed:22155184, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:22699938). In the absence of Wnt, forms a complex with AXIN1, AXIN2, APC, CSNK1A1 and GSK3B that promotes phosphorylation on N- terminal Ser and Thr residues and ubiquitination of CTNNB1 via BTRC and its subsequent degradation by the proteasome (PubMed:17524503, PubMed:18077326, PubMed:18086858, PubMed:18957423, PubMed:21262353, PubMed:22155184, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:22699938). In the presence of Wnt ligand, CTNNB1 is not ubiquitinated and accumulates in the nucleus, where it acts as a coactivator for transcription factors of the TCF/LEF family, leading to activate Wnt responsive genes (PubMed:17524503, PubMed:18077326, PubMed:18086858, PubMed:18957423, PubMed:21262353, PubMed:22155184, PubMed:22647378, PubMed:22699938). Also acts as a coactivator for other transcription factors, such as NR5A2 (PubMed:22187462). Promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition/mesenchymal to epithelial transition (EMT/MET) via driving transcription of CTNNB1/TCF-target genes (PubMed:29910125). Involved in the regulation of cell adhesion, as component of an E-cadherin:catenin adhesion complex (By similarity). Acts as a negative regulator of centrosome cohesion (PubMed:18086858). Involved in the CDK2/PTPN6/CTNNB1/CEACAM1 pathway of insulin internalization (PubMed:21262353). Blocks anoikis of malignant kidney and intestinal epithelial cells and promotes their anchorage-independent growth by down-regulating DAPK2 (PubMed:18957423). Disrupts PML function and PML- NB formation by inhibiting RANBP2-mediated sumoylation of PML (PubMed:22155184). Promotes neurogenesis by maintaining sympathetic neuroblasts within the cell cycle (By similarity). Involved in chondrocyte differentiation via interaction with SOX9: SOX9-binding competes with the binding sites of TCF/LEF within CTNNB1, thereby inhibiting the Wnt signaling (By similarity). Acts as a positive regulator of odontoblast differentiation during mesenchymal tooth germ formation, via promoting the transcription of differentiation factors such as LEF1, BMP2 and BMP4 (By similarity). Activity is repressed in a MSX1-mediated manner at the bell stage of mesenchymal tooth germ formation which prevents premature differentiation of odontoblasts (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:B6V8E6}. Cell junction, adherens junction Cell junction {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:B6V8E6}. Cell membrane. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole. Synapse {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q02248} Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, cilium basal body {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q02248}. Note=Colocalized with RAPGEF2 and TJP1 at cell-cell contacts (By similarity). Cytoplasmic when it is un-stable (highly phosphorylated) or bound to CDH1. Translocates to the nucleus when it is stabilized (low level of phosphorylation). Interaction with GLIS2 and MUC1 promotes nuclear translocation. Interaction with EMD inhibits nuclear localization. The majority of CTNNB1 is localized to the cell membrane. In interphase, colocalizes with CROCC between CEP250 puncta at the proximal end of centrioles, and this localization is dependent on CROCC and CEP250. In mitosis, when NEK2 activity increases, it localizes to centrosomes at spindle poles independent of CROCC. Colocalizes with CDK5 in the cell-cell contacts and plasma membrane of undifferentiated and differentiated neuroblastoma cells Interaction with FAM53B promotes translocation to the nucleus (PubMed:25183871). Translocates to the nucleus in the presence of SNAIL1 (By similarity). Ca(2+)-mediated localization to the cell membrane in dental epithelial cells is inhibited via WNT3A (By similarity). Localizes to cell-cell contacts as keratinocyte differentiation progresses (By similarity) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:B6V8E6, ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q02248, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25183871} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in several hair follicle cell types: basal and peripheral matrix cells, and cells of the outer and inner root sheaths. Expressed in colon. Present in cortical neurons (at protein level). Expressed in breast cancer tissues (at protein level) (PubMed:29367600). |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
The protein encoded by this gene is part of a complex of proteins that constitute adherens junctions (AJs). AJs are necessary for the creation and maintenance of epithelial cell layers by regulating cell growth and adhesion between cells. The encoded protein also anchors the actin cytoskeleton and may be responsible for transmitting the contact inhibition signal that causes cells to stop dividing once the epithelial sheet is complete. Finally, this protein binds to the product of the APC gene, which is mutated in adenomatous polyposis of the colon. Mutations in this gene are a cause of colorectal cancer (CRC), pilomatrixoma (PTR), medulloblastoma (MDB), and ovarian cancer. Three transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene.
REFERENCES
Huang, W., et al. Mol. Cell. Biol. 30(19):4575-4594(2010)
Chairoungdua, A., et al. J. Cell Biol. 190(6):1079-1091(2010)
Mirza, M.K., et al. J. Exp. Med. 207(8):1675-1685(2010)
Guo, Q., et al. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 42(7):450-456(2010)
Teng, Y., et al. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 90(14):988-992(2010)
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。