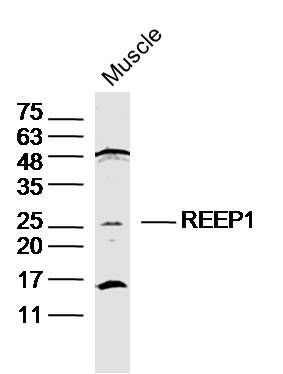
REEP1 Polyclonal Antibody
Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
Application
| WB, IHC-P, IHC-F, IF, ICC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9H902 |
| Reactivity | Rat, Pig, Dog, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 22255 Da |
| Physical State | Liquid |
| Immunogen | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human REEP1 |
| Epitope Specificity | 53-150/201 |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Purity | affinity purified by Protein A |
| Buffer | 0.01M TBS (pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.02% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| SUBCELLULAR LOCATION | Membrane. Mitochondrion membrane; Multi-passmembrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum. |
| SIMILARITY | Belongs to the DP1 family. |
| SUBUNIT | Interacts with SPAST and ATL1; it preferentiallyinteracts with SPAST isoform 1. Interacts (via C-terminus) withmicrotubules. Interacts with odorant receptor proteins |
| Post-translational modifications | Belongs to the DP1 family. |
| DISEASE | Defects in REEP1 are the cause of spastic paraplegia autosomal dominant type 31 (SPG31) [MIM:610250]. Spastic paraplegia is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a slow, gradual, progressive weakness and spasticity of the lower limbs. Rate of progression and the severity of symptoms are quite variable. Initial symptoms may include difficulty with balance, weakness and stiffness in the legs, muscle spasms, and dragging the toes when walking. In some forms of the disorder, bladder symptoms (such as incontinence) may appear, or the weakness and stiffness may spread to other parts of the body. |
| Important Note | This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |
| Background Descriptions | Transport of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) to the cell surface membrane is critical for receptor-ligand recognition. Mammalian GPCR odorant receptors (ORs), when heterologously expressed in cells, are poorly expressed on the cell surface. REEP1 (receptor expression-enhancing protein 1), is a 201 amino acid multi-pass mitochondrion membrane protein that belongs to the DP1 family. REEP1 interacts with odorant receptor proteins and may enhance the cell surface expression of odorant receptors. Mutations in the REEP1 gene are the third most common cause of hereditary spastic paraplegia (HSP) after spastin and atlastin gene mutations. Mutations in the REEP1 gene also cause spastic paraplegia autosomal dominant type 31, a neurodegenerative disorder. The REEP1 gene is conserved in chimpanzee, dog, cow, mouse, rat, chicken, zebrafish, A.thaliana and rice, and maps to human chromosome 2p11.2. |
| Gene ID | 65055 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Receptor expression-enhancing protein 1, Spastic paraplegia 31 protein, REEP1, C2orf23, SPG31 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:23969831} |
| Dilution | WB=1:500-2000,IHC-P=1:100-500,IHC-F=1:100-500,ICC=1:100-500,IF=1:100-500,ELISA=1:5000-10000 |
| Format | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide and 50% Glyce |
| Storage | Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. When reconstituted in sterile pH 7.4 0.01M PBS or diluent of antibody the antibody is stable for at least two weeks at 2-4 °C. |
| Name | REEP1 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | C2orf23, SPG31 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:23969 |
| Function | Required for endoplasmic reticulum (ER) network formation, shaping and remodeling; it links ER tubules to the cytoskeleton. May also enhance the cell surface expression of odorant receptors (PubMed:20200447). May play a role in long-term axonal maintenance (PubMed:24478229). |
| Cellular Location | Membrane. Mitochondrion membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Endoplasmic reticulum Note=Localizes to endoplasmic reticulum tubular network |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in circumvallate papillae and testis. |
Research Areas
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。