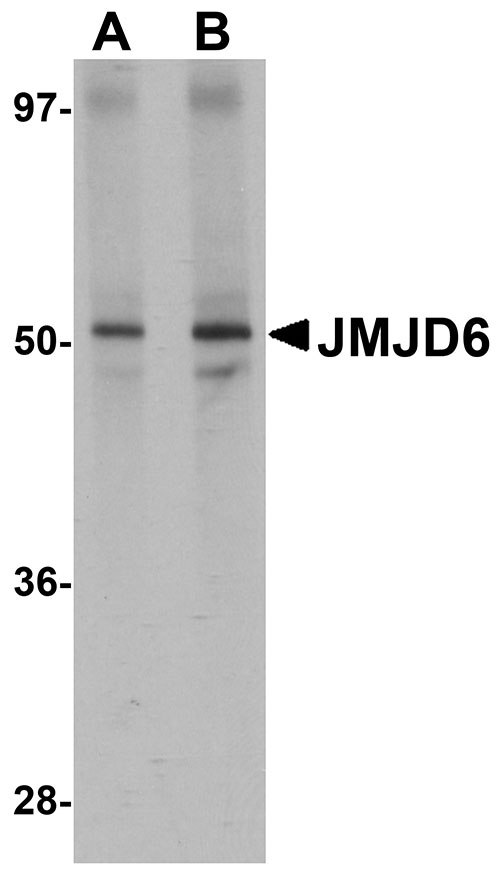
JMJD6 Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, E, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q6NYC1 |
| Other Accession | Q6NYC1, 67461014 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 46462 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Application Notes | JMJD6 antibody can be used for detection of JMJD6 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 2.5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 23210 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Bifunctional arginine demethylase and lysyl-hydroxylase JMJD6, 1.14.11.-, Histone arginine demethylase JMJD6, JmjC domain-containing protein 6, Jumonji domain-containing protein 6, Lysyl-hydroxylase JMJD6, Peptide-lysine 5-dioxygenase JMJD6, Phosphatidylserine receptor, Protein PTDSR, JMJD6, KIAA0585, PTDSR |
| Target/Specificity | JMJD6; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | JMJD6 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | JMJD6 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | JMJD6 (HGNC:19355) |
|---|---|
| Function | Dioxygenase that can both act as a arginine demethylase and a lysyl-hydroxylase (PubMed:17947579, PubMed:20684070, PubMed:21060799, PubMed:22189873, PubMed:24498420). Acts as a lysyl-hydroxylase that catalyzes 5-hydroxylation on specific lysine residues of target proteins such as U2AF2/U2AF65 and LUC7L2. Regulates RNA splicing by mediating 5-hydroxylation of U2AF2/U2AF65, affecting the pre-mRNA splicing activity of U2AF2/U2AF65 (PubMed:19574390). Hydroxylates its own N-terminus, which is required for homooligomerization (PubMed:22189873). Plays a role in the regulation of nucleolar liquid- liquid phase separation (LLPS) by post-translationally modifying LIAT1 at its lysine-rich domain which inhibits LIAT1 nucleolar targeting (By similarity). In addition to peptidyl-lysine 5-dioxygenase activity, may act as an RNA hydroxylase, as suggested by its ability to bind single strand RNA (PubMed:20679243, PubMed:29176719). Also acts as an arginine demethylase which preferentially demethylates asymmetric dimethylation (PubMed:17947579, PubMed:24360279, PubMed:24498420). Demethylates histone H3 at 'Arg-2' (H3R2me) and histone H4 at 'Arg-3' (H4R3me), including mono-, symmetric di- and asymmetric dimethylated forms, thereby playing a role in histone code (PubMed:17947579, PubMed:24360279). However, histone arginine demethylation may not constitute the primary activity in vivo (PubMed:17947579, PubMed:21060799, PubMed:22189873). In collaboration with BRD4, interacts with the positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) complex in its active form to regulate polymerase II promoter-proximal pause release for transcriptional activation of a large cohort of genes. On distal enhancers, so called anti-pause enhancers, demethylates both histone H4R3me2 and the methyl cap of 7SKsnRNA leading to the dismissal of the 7SKsnRNA:HEXIM1 inhibitor complex. After removal of repressive marks, the complex BRD4:JMJD6 attract and retain the P-TEFb complex on chromatin, leading to its activation, promoter-proximal polymerase II pause release, and transcriptional activation (PubMed:24360279). Demethylates other arginine methylated- proteins such as ESR1 (PubMed:24498420). Has no histone lysine demethylase activity (PubMed:21060799). Required for differentiation of multiple organs during embryogenesis. Acts as a key regulator of hematopoietic differentiation: required for angiogenic sprouting by regulating the pre-mRNA splicing activity of U2AF2/U2AF65 (By similarity). Seems to be necessary for the regulation of macrophage cytokine responses (PubMed:15622002). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Nucleus, nucleolus. Cytoplasm. Note=Mainly found throughout the nucleoplasm outside of regions containing heterochromatic DNA, with some localization in nucleolus. During mitosis, excluded from the nucleus and reappears in the telophase of the cell cycle. |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in the heart, skeletal muscle and kidney. Expressed at moderate or low level in brain, placenta, lung, liver, pancreas, spleen, thymus, prostate, testis and ovary. Up- regulated in many patients with chronic pancreatitis. Expressed in nursing thymic epithelial cells. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
JMJD6 Antibody: The jumonji domain-containing protein (JMJD) family is defined by the presence of the JmjC domain that is observed in several diverse species. JMJD6 was initially identified as a membrane protein that participates in phagocytosis but recent studies have shown that it has other functions when it is expressed in the cytosol and nucleus. JMJD6 is thought to play important roles in regulation of development and differentiation as knockdown experiments in mice resulted in neonatal lethality with severe defects in the morphology of numerous organs. JMJD6 also can catalyze the lysyl-hydroxylation of U2AF65, a protein involved with RNA splicing, suggesting that some of the functions attributed to JMJD6 may be due to its regulatory activity of RNA splicing.
REFERENCES
Takeuchi T, Watanabe Y, Takano-Shimizu T, et al. Roles of jumonji and jumonji family genes in chromatin regulation and development. Dev. Dyn.2006; 235:2449-59.
Fadok VA, Bratton DL, Rose DM, et al. A receptor for phosphatidylserine-specific clearance of apoptotic cells. Nature2000; 405:85-90.
Zakharova L, Dadsetan S, and Fomina AF. Endogenous JMJD6 gene product is expressed at the cell surface and regulates phagocytosis in immature monocyte-like activated THP-1 cells. J. Cell. Phys.2009; 221:84-91.
Bose J, Gruber AD, Helming L, et al. The phosphatidylserine receptor has essential functions during embryogenesis but not in apoptotic cell removal. J. Biol.2004; 3:15.
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。