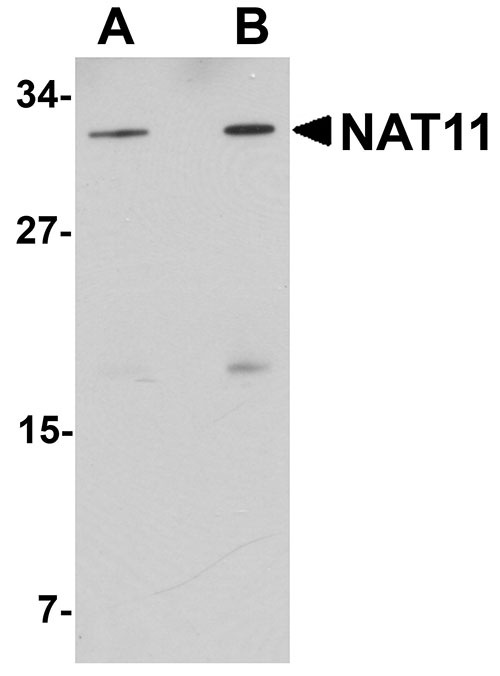
NAT11 Antibody
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| WB, IF, E, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q86UY6 |
| Other Accession | NP_079047, 189571650 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 27194 Da |
| Concentration (mg/ml) | 1 mg/mL |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Application Notes | NAT11 antibody can be used for detection of NAT11 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 79829 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | N-alpha-acetyltransferase 40, 2.3.1.-, N-acetyltransferase 11, NatD catalytic subunit, NAA40, NAT11 |
| Target/Specificity | NAA40; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | NAT11 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | NAT11 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | NAA40 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:19660095, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:25845} |
|---|---|
| Function | N-alpha-acetyltransferase that specifically mediates the acetylation of the N-terminal residues of histones H4 and H2A (PubMed:21935442, PubMed:25619998). In contrast to other N-alpha- acetyltransferase, has a very specific selectivity for histones H4 and H2A N-terminus and specifically recognizes the 'Ser-Gly-Arg-Gly sequence' (PubMed:21935442, PubMed:25619998). Acts as a negative regulator of apoptosis (PubMed:26666750). May play a role in hepatic lipid metabolism (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Nucleus |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed; with the highest expression level in liver and the lowest expression in brain (at protein level) |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
NAT11 Antibody: N-terminal acetylation is one of the most common protein modifications in eukaryotes, occurring on approximately 57% and 84% on yeast and human proteins respectively. There are several N-terminal acetylating enzyme complexes (NatA - NatE). Unlike the other complexes, NatD is composed of a single protein, NAT11, and has recently been described to acetylate the Serine N-termini of histones H2A and H4 in yeast. The role these modifications play is unknown; yeast that do not express NAT11 grow at normal rates and have no observable phenotypes. The role of the human homolog is likewise unknown.
REFERENCES
Arnesen T, Van Damme P, Polevoda B, et al. Proteomics analyses reveal the evolutionary conservation and divergence of N-terminal acetyltransferases from yeast and humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA2009; 106:8157-62.
OK Song, Wang X, Waterborg JH, et al. An Nalpha-acetyl-transferase responsible for acetylation of the N-terminal residues of histones H4 and H2A. J. Biol. Chem.2003; 278:38109-1
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。