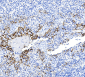
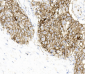
PD-L1-Rmab
Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Mab)
- 产品详情
- 实验流程
- 背景知识
Application
| IHC-P, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9NZQ7 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 33275 Da |
| Gene ID | 29126 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1, PD-L1, PDCD1 ligand 1, Programmed death ligand 1, B7 homolog 1, B7-H1, CD274, CD274, B7H1, PDCD1L1, PDCD1LG1, PDL1, PDL-1 |
| Target/Specificity | Recombinant anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody recognizes endogenous levels of total PD-L1 protein. |
| Dilution | IHC-P~~1:1000 E~~Use at an assay dependent concentration. |
| Format | Purified recombination monoclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.05% (W/V) Proclin300, and 0.05% BSA. This antibody is purified through a protein A column. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | PD-L1-Rmab is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CD274 (HGNC:17635) |
|---|---|
| Function | Plays a critical role in induction and maintenance of immune tolerance to self (PubMed:11015443, PubMed:28813410, PubMed:28813417, PubMed:31399419). As a ligand for the inhibitory receptor PDCD1/PD-1, modulates the activation threshold of T-cells and limits T-cell effector response (PubMed:11015443, PubMed:28813410, PubMed:28813417, PubMed:36727298). Through a yet unknown activating receptor, may costimulate T-cell subsets that predominantly produce interleukin-10 (IL10) (PubMed:10581077). Can also act as a transcription coactivator: in response to hypoxia, translocates into the nucleus via its interaction with phosphorylated STAT3 and promotes transcription of GSDMC, leading to pyroptosis (PubMed:32929201). |
| Cellular Location | Cell membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Early endosome membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Recycling endosome membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Nucleus. Note=Associates with CMTM6 at recycling endosomes, where it is protected from being targeted for lysosomal degradation (PubMed:28813417). Translocates to the nucleus in response to hypoxia via its interaction with phosphorylated STAT3 (PubMed:32929201). [Isoform 2]: Endomembrane system; Single-pass type I membrane protein |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in the heart, skeletal muscle, placenta and lung. Weakly expressed in the thymus, spleen, kidney and liver. Expressed on activated T- and B-cells, dendritic cells, keratinocytes and monocytes. |
For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
BACKGROUND
Programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1, B7-H1, CD274) is a member of the B7 family of cell surface ligands that regulate T cell activation and immune responses. The PD-L1 ligand binds the PD-1 transmembrane receptor and inhibits T cell activation. PD-L1 was discovered following a search for novel B7 protein homologs and was later shown to be expressed by antigen presenting cells, activated T cells, and tissues including placenta, heart, and lung. Similar in structure to related B7 family members, PD-L1 protein contains extracellular IgV and IgC domains and a short, cytoplasmic region. Research studies demonstrate that PD-L1 is expressed in several tumor types, including melanoma, ovary, colon, lung, breast, and renal cell carcinomas. Expression of PD-L1 in cancer is associated with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, which mediate PD-L1 expression through the release of interferon gamma. Additional research links PD-L1 expression to cancers associated with viral infections. Involved in the costimulatory signal, essential for T- cell proliferation and production of IL10 and IFNG, in an IL2- dependent and a PDCD1-independent manner. Interaction with PDCD1 inhibits T-cell proliferation and cytokine production.
REFERENCES
Dong H.,et al.Nat. Med. 5:1365-1369(1999).
Freeman G.J.,et al.J. Exp. Med. 192:1027-1034(2000).
He X.-H.,et al.Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 26:462-468(2005).
Chi X.-Y.,et al.Submitted (NOV-2005) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Ota T.,et al.Nat. Genet. 36:40-45(2004).
Dong, H. et al. (1999) Nat Med 5, 1365-9.
Freeman, G.J. et al. (2000) J Exp Med 192, 1027-34.
Liang, S.C. et al. (2003) Eur J Immunol 33, 2706-16.
Dong, H. et al. (2002) Nat Med 8, 793-800.
Thompson, R.H. et al. (2006) Cancer Res 66, 3381-5.
Pardoll, D.M. (2012) Nat Rev Cancer 12, 252-64.
Taube, J.M. et al. (2012) Sci Transl Med 4, 127ra37.
Lyford-Pike, S. et al. (2013) Cancer Res 73, 1733-41.
Chen, B.J. et al. (2013) Clin Cancer Res 19, 3462-73.
Wimberly, H. et al. (2014) Cancer Immunol Res , .
终于等到您。ABCEPTA(百远生物)抗体产品。
点击下方“我要评价 ”按钮提交您的反馈信息,您的反馈和评价是我们最宝贵的财富之一,
我们将在1-3个工作日内处理您的反馈信息。
如有疑问,联系:0512-88856768 tech-china@abcepta.com.























 癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。
癌症的基本特征包括细胞增殖、血管生成、迁移、凋亡逃避机制和细胞永生等。找到癌症发生过程中这些通路的关键标记物和对应的抗体用于检测至关重要。 为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。
为您推荐一个泛素化位点预测神器——泛素化分析工具,可以为您的蛋白的泛素化位点作出预测和评分。 细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。
细胞自噬受体图形绘图工具为你的蛋白的细胞受体结合位点作出预测和评分,识别结合到自噬通路中的蛋白是非常重要的,便于让我们理解自噬在正常生理、病理过程中的作用,如发育、细胞分化、神经退化性疾病、压力条件下、感染和癌症。